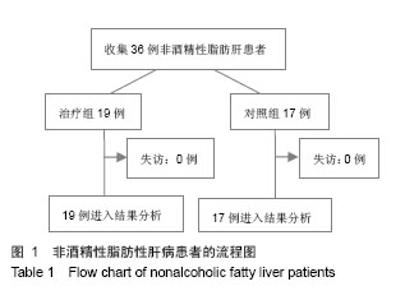
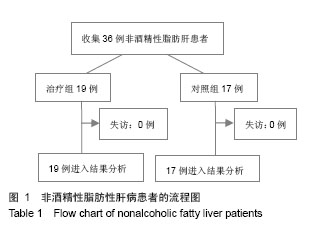
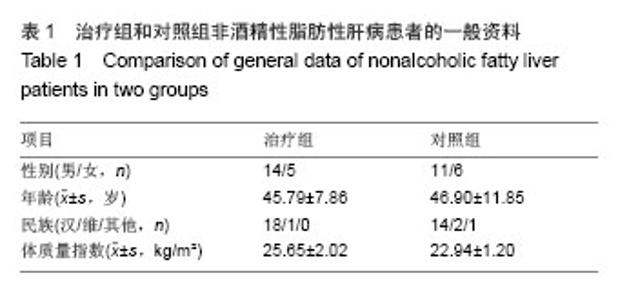
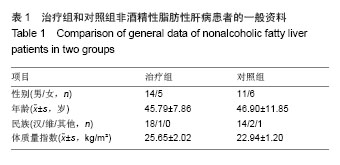
| [1]Sanyal AJ; American Gastroenterological Association. AGA technical review on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(5):1705-1725.
[2]邓笑伟,刘冰,马春梅,等.血清铁蛋白水平与非酒精性脂肪肝及相关危险因素关系[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2012,26(3): 243-244.
[3]Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM. Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34(3):274-285.
[4]郑刚.非酒精性脂肪性肝病与肝癌关系研究进展[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2012,21(3):216-219.
[5]Duan XY, Qiao L, Fan JG. Clinical features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012;11(1):18-27.
[6]Lall CG, Aisen AM, Bansal N, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(4):993-1002.
[7]邹傲.非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关危险因素研究进展[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2012,21(1):92-94.
[8]de Alwis NM, Day CP. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the mist gradually clears. J Hepatol. 2008;48 Suppl 1:S104-112.
[9]Villanova N, Moscatiello S, Ramilli S, et al. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk profile in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;42(2):473-480.
[10]Targher G, Bertolini L, Scala L, et al. Non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis and its relation to increased plasma biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in non-diabetic men. Role of visceral adipose tissue. Diabet Med. 2005;22(10): 1354-1358.
[11]Huang XD, Fan Y, Zhang H, et al. Serum leptin and soluble leptin receptor in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(18):2888-2893.
[12]范彦,黄晓东,张恒,等.非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者血清瘦素与胰岛素抵抗的关系[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2010,19(6):502-504.
[13]Tilg H. Adipocytokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: key players regulating steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(17):1893-1895.
[14]王霞,梁英,闫杰,等.血清瘦素与非酒精性脂肪性肝病及其相关因素分析[J].中国临床医生,2012,40(3):48-51.
[15]赵严,孟娟娟,刘近春,等.非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者内毒素、瘦素、IL-6及IL-8水平测定[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2009,18(9): 849-851.
[16]范建高,曾民德.脂肪性肝病[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005: 306-321.
[17]Zamora ZB, Borrego A, López OY, et al. Effects of ozone oxidative preconditioning on TNF-alpha release and antioxidant-prooxidant intracellular balance in mice during endotoxic shock. Mediators Inflamm. 2005; 2005(1):16-22.
[18]中华医学会肝脏病学分会脂肪肝和酒精性肝病学组.非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊疗指南[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2010,11(4):73.
[19]Younossi ZM, Diehl AM, Ong JP. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an agenda for clinical research. Hepatology. 2002;35(4):746-752.
[20]Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two "hits"? Gastroenterology. 1998;114(4):842-845.
[21]Larini A, Bianchi L, Bocci V. The ozone tolerance: I) Enhancement of antioxidant enzymes is ozone dose-dependent in Jurkat cells. Free Radic Res. 2003; 37(11):1163-1168.
[22]Zamora ZB, Borrego A, López OY, et al. Effects of ozone oxidative preconditioning on TNF-alpha release and antioxidant-prooxidant intracellular balance in mice during endotoxic shock. Mediators Inflamm. 2005;2005(1):16-22.
[23]Bocci V.臭氧治疗学[M].李庆祥,王燕申,译.北京:北京大学医学出版社,2006.
[24]Bocci V, Di Paolo N. Oxygen-ozone therapy in medicine: an update. Blood Purif. 2009;28(4):373-376.
[25]高连宝.医用臭氧的临床应用进展[J].天津医科大学学报, 2011, 17(2):278-280.
[26]Lu W, Li YH, He XF. Treatment of large lumbar disc herniation with percutaneous ozone injection via the posterior-lateral route and inner margin of the facet joint. World J Radiol. 2010;2(3):109-112.
[27]Koca K, Yurtta? Y, Y?ld?z C, et al. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen and ozone preconditioning on oxidative/nitrosative stress induced by tourniquet ischemia/reperfusion in rat skeletal muscle. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44(6):476-483.
[28]刘建英,王文,单素英,等.低温等离子髓核成形术联合臭氧治疗颈椎间盘突出症临床疗效分析[J].中国疼痛医学杂志, 2012,18(3): 130-134.
[29]王文涛,杨芳,贺利军,等.C型臂下射频靶点热凝联合臭氧消融术治疗颈椎病319例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2012,12(8): 1903-1904.
[30]俞志坚,罗文志,王保安.后入路经椎管及硬膜囊臭氧靶点注射治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].南方医科大学学报,2012,32(2):243-246.
[31]王炳良,耿玉强,乔乃春,等.大剂量胶原酶联合臭氧盘内注射治疗巨大型腰椎间盘突出症48例疗效分析[J].蚌埠医学院学报, 2012, 37(2):183-188.
[32]菅新民,周建华,张弦,等.切吸联合臭氧治疗腰椎间盘突出症的早期疗效[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2012,21(4):343-347.
[33]王欣,王坦新,李生军.胶原酶联合臭氧治疗腰椎间盘突出症200例的疗效观察及护理[J].中国医药科学,2012,2(2):164-167.
[34]刘娜,吴大胜.宫小文,等.射频消融联合臭氧髓核溶解术与无创治疗颈椎间盘突出症的疗效对比研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2012, 18(1):63-64.
[35]余留森,张建华,刘艳玲,等.臭氧配合高渗盐注射治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].吉林医学,2012,33(1):108-109.
[36]梅敦成,黄恒,杨小龙,等.臭氧联合玻璃酸钠关节腔注射治疗髋骨关节炎30例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(2):54-55.
[37]陈晓君,吴小宝,仇艳艳.医用臭氧联合盐酸利多卡因局部注射治疗肩周炎56例临床观察[J].临床军医杂志,2012,40(1):220-221.
[38]谭利,王池凤,刘伟波,等.医用臭氧治疗膝关节骨关节炎效果观察[J].解放军医药杂志,2012,24(1):27-29.
[39]陈潇.探讨不同浓度臭氧治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2012,18(1):57-58.
[40]周钰,杨晓嫒,许晓冬,等.关节腔臭氧注射治疗膝关节骨性关节炎对关节液中白细胞介素-1β、肿瘤坏死因子-α的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2012,27(1):73-74.
[41]扎西草,王薇,阿孜古丽,等.臭氧联合痛点注射治疗骨关节炎110例临床分析[J].新疆医学,2011,41:90-92.
[42]莫淡荷.微波联合臭氧治疗宫颈炎临床体会[J].中国当代医药, 2012, 19(3):177-178.
[43]陈海英.医用臭氧治疗仪治疗阴道炎的应用研究[J].当代医学, 2011,17(36):154-155.
[44]文泽华.臭氧治疗外阴阴道假丝酵母菌病的疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2012,5(3):120-121.
[45]杨淑盈,单岩.糖尿病足创面护理的研究进展[J].全科护理, 2011 9(35):3288-3290.
[46]杨飞,姜建威,王鹏,等.膝下动脉成形术联合臭氧气浴治疗糖尿病足(附9例报告)[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2011,31(11): 1688-1689.
[47]金玉芳,杨玉琴.高压臭氧大自血治疗下肢深静脉血栓形成128例临床护理[J].齐鲁护理杂志,2012,18(1):80-81.
[48]段蓉.臭氧治疗脑梗死80例疗效观察[J].中国民康医学, 2012, 24(1): 47-48.
[49]徐维佳,肖元.高压臭氧大自血灌注治疗脑血管疾病临床研究[J].中外医学研究,2011,9(23):24-25.
[50]郭亚兵.医用臭氧在内科临床中的应用[J].中华实验和临床感染病杂志:电子版,2008,2(1):106.
[51]包颖,陈晓虹,姜海涛.臭氧大自血疗法联合辛伐他汀对缺血性卒中患者血脂水平的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2011,28(4): 353-354.
[52]赵子粼,鄢莉,黄好华,等.臭氧自血疗法对代谢综合征患者的临床疗效观察[J].四川医学,2010,31(10):1499.
[53]李勇燕,贺清明.臭氧在高血压患者治疗护理中的应用[J].吉林医学,2011,32(20):4241-4242.
[54]覃善都,罗建春,郭磊,等.高血压伴高粘血症患者臭氧置血治疗临床观察[J].华南国防医学杂志,2011,25(1):74-75.
[55]杨建锋,陈芝芸,项柏康,等.非酒精性脂肪肝患者血清瘦素的变化[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2004,24(12):752-753.
[56]Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994; 372(6505):425-432.
[57]卫建筠,杨海红,曾文铤.非酒精性脂肪肝患者血清瘦素水平与肝纤维化关系研究[J].临床医学工程,2009,16(4):46-47.
[58]Eberting CL, Javor E, Gorden P, et al. Insulin resistance, acanthosis nigricans, and hypertriglyceridemia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(2):341-344.
[59]Bugianesi E, Zannoni C, Vanni E, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver and insulin resistance: a cause-effect relationship? Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36(3):165-173. |